This post will build on the Introduction to Graph Query Language post where we were looking at the relationship between a Customer and Tender (mode of payment) as used in Transactions. In this post, we will use Property Graph to solve a Transitive Closure problem.
To recap:
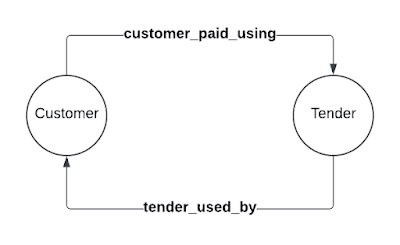
- Customer may use a Tender (mode of payment e.g. Credit Card, Gift Card etc);
- A Tender (mode of payment) can be used by Customer
It is Many to Many Relationship, i.e. a Customer may use multiple Credit Card, and a single Credit Card may be shared by multiple Customer e.g. Husband and Wife
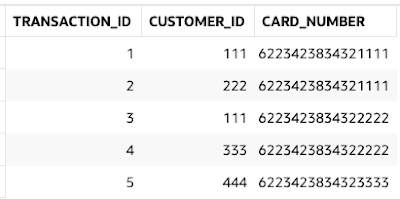
We need to create a Database View that can capture this many-to-many association as a network which is a single record. The single records should have all the Credit Cards by all the Customers that have used those Credit Card. Let’s illustrate this with a sample with the following Transactions and the Customers and the Tenders (Credit Cards) they used
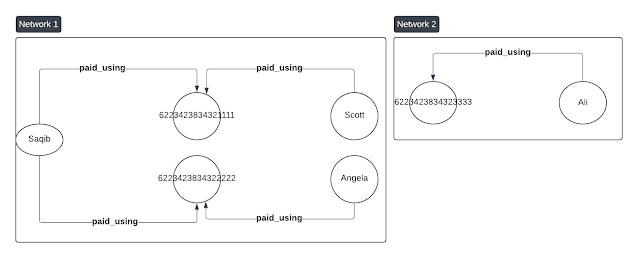
We will end up with the following Network(s):
In a tabular format:

This is a classic Transitive Closure problem.
We will use the SHARED_TENDER table we created in the Introduction to Graph Query Language post and build a Property Graph on it to represent the Customer to Customer relationship.
create table shared_tender as
SELECT distinct *
FROM GRAPH_TABLE( PAYMENT_TENDER_GRAPH
MATCH (customer1 is customer) - [e1 is customer_paid_using] ->
(shared_tender is tender) <- [e2 is customer_paid_using]
- (customer2 is customer)
where customer1.customer_id != customer2.customer_id
COLUMNS (customer1.customer_id as customer1_id
, customer1.first_name as customer_1_name
, shared_tender.card_number as shared_tender
, customer2.customer_id as customer2_id
, customer2.first_name as customer_2_name)
);
Create the property graph:
CREATE or replace PROPERTY GRAPH CUSTOMER_CUSTOMER_RELATIONSHIP
VERTEX TABLES (
customer KEY (customer_id) PROPERTIES ARE ALL COLUMNS
)
EDGE TABLES (
SHARED_TENDER as customer_is_related_to
KEY (customer1_id, shared_tender, customer2_id)
SOURCE KEY (customer1_id ) REFERENCES customer(customer_id)
DESTINATION KEY (customer2_id ) REFERENCES customer(customer_id)
PROPERTIES (customer1_id, customer2_id, shared_tender)
);
Next we will use the following Graph Query to output the desired Network in a Tabular format.
SELECT distinct
listagg(distinct customer2_id, ', ') as customer_ids
, listagg(distinct TRANSACTIONS.card_number, ', ') as credit_card_numbers
FROM GRAPH_TABLE(
CUSTOMER_CUSTOMER_RELATIONSHIP
MATCH (customer1 is customer) -
[e1 is customer_is_related_to]->{,5} (customer2 is customer)
COLUMNS (customer1.customer_id as customer1_id
, customer2.customer_id as customer2_id)
)
inner join TRANSACTIONS on customer2_id = TRANSACTIONS.customer_id
group by customer1_id;

As you can see, this Transitive Closure problem was solvable using a Property Graph.
Note: MATCH can find variable lengths patterns. To find relationship between customer up to 5 Levels we use : [e1 is customer_is_related_to]->{,5} (customer2 is customer)
Available length patterns:
{n} : exactly n steps
{n.m} : between n and m steps (inclusive)
{,n} : up to n steps (from 0, inclusive)
? : 0 or 1 steps
Acknowledgments:
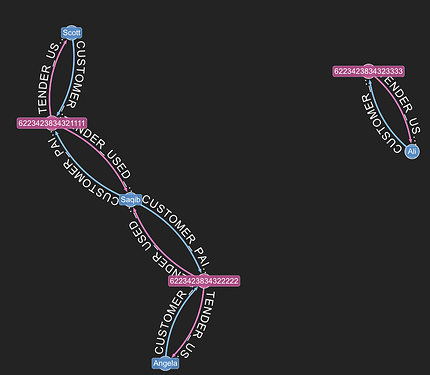
- Property Graph visualizations were created using G.V() – Graph Database Client & Visualization Tool