Snowflake’s versatile FLATTEN function is used to expand nested data, such as semi-structured data, into a tabular format that can be more easily manipulated with SQL. It ‘explodes’ complex data types like VARIANT, OBJECT, or ARRAY, turning one row into multiple rows by expanding nested arrays or objects. This transformation makes semi-structured data more accessible for querying and analysis.
The FLATTEN function is used by many developers without realizing it supports two modes: ARRAY and OBJECT.
The following examples will demonstrate these two MODES on a similar dataset.
Imagine a dataset with Orders and Order Lines. In one case the Order Lines are Nested OBJECTs and in the other case they are defined as an ARRAY
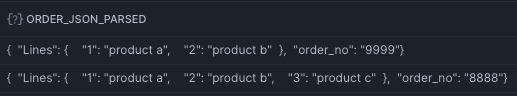
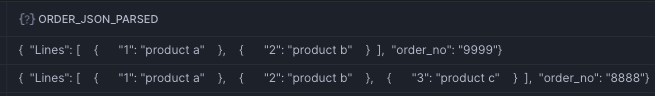
Note that the above two JSONs are fundamentally different. One makes use of ARRAY for Order Lines and where in the other case the Order Lines are nested Objects. FLATTEN supports flattening both of the JSONs, however you have to select the correct MODE.
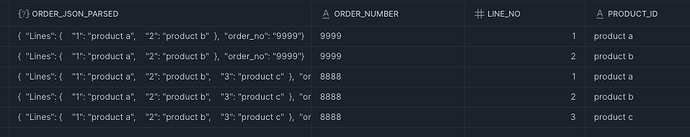
Let’s start with the example where the Order Lines are a Nested Objects, we will use
MODE => 'OBJECT' in the FLATTEN function:
with orders as (
select '{"order_no": "9999", "Lines": {"1": "product a", "2": "product b"}}' as order_json
union all
select '{"order_no": "8888", "Lines": {"1": "product a", "2": "product b", "3": "product c"}}'
)
select
parse_json(order_json) as order_json_parsed
, order_json_parsed:"order_no"::string as order_number
, flattened.key::int
, flattened.value::string
from orders
, lateral flatten(input => order_json_parsed:"Lines", MODE => 'OBJECT') as flattened
;
Notice that since the Lines are just Key-Value OBJECTs, we can simply access then using the f.key and f.value once FLATTENed
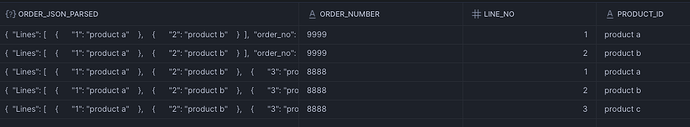
Now let’s FLATTEN the scenario where the Order Lines are in an array. For this we will use the MODE => 'ARRAY' in the FLATTEN function.
with orders as (
select '{"order_no": "9999", "Lines": [{"1": "product a"}, {"2": "product b"}]}' as order_json
union all
select '{"order_no": "8888", "Lines": [{"1": "product a"}, {"2": "product b"}, {"3": "product c"}]}'
)
select
parse_json(order_json) as order_json_parsed
, order_json_parsed:"order_no"::string as order_number
, object_keys(flattened.value)[0]::int as line_no
, f.value[object_keys(flattened.value)[0]]::string as product_id
from orders
, lateral flatten(input => order_json_parsed:"Lines", MODE => 'ARRAY') as flattened
;
Notice that since this is an ARRAY of Objects we have to use object_keys() function to get the KEY and the VALUE from each Object